Classification by a Neural Network using Keras
Overview
Teaching: 30-60 min
Exercises: 40-45 minQuestions
What is a neural network?
How do I compose a Neural Network using Keras?
How do I train this network on a dataset?
How do I get insight into learning process?
How do I measure the performance of the network?
Objectives
Use the deep learning workflow to structure the notebook
Explore the dataset using pandas and seaborn
Use one-hot encoding to prepare data for classification in Keras
Describe a fully connected layer
Implement a fully connected layer with Keras
Use Keras to train a small fully connected network on prepared data
Interpret the loss curve of the training process
Use a confusion matrix to measure the trained networks’ performance on a test set
Introduction
In this episode we will learn how to create and train a Neural Network using Keras to solve a simple classification task.
The goal of this episode is to quickly get your hands dirty (no.. not from fieldwork) in actually defining and training a neural network, without going into depth of how neural networks work on a technical or mathematical level. We want you to go through the most commonly used deep learning workflow that was covered in the introduction. As a reminder below are the steps of the deep learning workflow:
- Formulate / Outline the problem
- Identify inputs and outputs
- Prepare data
- Choose a pretrained model or start building architecture from scratch
- Choose a loss function and optimizer
- Train the model
- Perform a Prediction/Classification
- Measure performance
- Tune hyperparameters
- Save model
In this episode we will focus on a minimal example for each of these steps, later episodes will build on this knowledge to go into greater depth for some or all of these steps.
GPU usage
For this lesson having a GPU (graphics card) available is not needed. We specifically use very small toy problems so that you do not need one. However, Keras will use your GPU automatically when it is available. Using a GPU becomes necessary when tackling larger datasets or complex problems which require a more complex Neural Network.
1. Formulate/outline the problem: classification
In this episode we will be using a subset of the below the surface dataset of which the original dataset can be downloaded as csv file here.
Data processing
To make the dataset suitable for an English Audience the column names have been translated from Dutch. Furthermore
Furthermore, the various fields in the dataset have been assessed ans classified in the following criteria:
- Adminstrative (e.g. find number, projectnumber, archaeological unit etc.)
- Measurement (length, weight, diameter etc. )
- Characteristic (characteristics of the object which does not necessaryly be done by an expert, like color or type of blade, decoration technique)
- Interpretation (Classification by an expert preferably to a reference collection / typochronology)
The classification was done on this file from the project and based on doman knowledge by Maurice de Kleijn. The result of this assessment can be found here.
Note that the distinction between Characteristic and Interpretation is a bit arbitrary
For this workshop we decided to look at ceramics. Since the aim is to automatically categorize data based on a variety of characteristics we decided to look at ceramics and see if we can train a neural network that distinguishes ceramics that are cateogorized as “plate, dish, bowl” from ceramics that are categorized as “drinking” based on non interpreted measurements on the dimensions (i.e. height and width), surface treatment and type of material. We thus try to see if the experts could be replaced by our neural nework. Please note, that we have simplified the question and that we the aim of this analysis is purely educational.
The subest has been created based on the a python script, which can be accessed here
The subset that the script created can ben accessed here). Please make sure to download this one (the other links are just a reference).
We will use this dataset to train a neural network which can classify the second level of the functional classification ( of the archeological artefect, based on certain features.
Goal
The goal is to predict the second level of functional classification using the attributes available in this dataset.
2. Identify inputs and outputs
To identify the inputs and outputs that we will use to design the neural network we need to familiarize ourselves with the dataset. This step is sometimes also called data exploration.
We will start by importing the pandas library that will help us read the dataset from the .csv file. Pandas is a fast, powerful, flexible and easy to use open source data analysis and manipulation tool, built on top of the Python programming language.
import pandas as pd
We can load the dataset using
ds = pd.read_csv('data/subset_ceramics_v30032023.csv')
This will give you a pandas dataframe which contains the data.
Inspect Dataset
Inspect the dataset.
- What are the different features called in the dataframe?
- Are the target classes of the dataset stored as numbers or strings?
- How many samples does this dataset have?
- How many NaN (Not a Number) are there for each feature? Tip: Use pandas functions: head describe unique isna sum
Solution
1. Using the pandas
headfunction you can see the names of the features. Using thedescribefunction we can also see some statistics for the numeric columnsds.head()ds.describe()2. We can get the unique values in the
l2_classcolumn using theuniquefunction of pandas. It shows the target class is stored as a string and has 3 unique values. This type of column is usually called a ‘categorical’ column.ds["l2_class"].unique()array(['Food consumption: plate, dish, bowl', 'Consumption: drinking', 'Food preparation: cooking - and hearth utensils', 'Food preparation and consumption: various parts of kitchenware', 'Consumption of tobacco and stimulants', 'Consumption of food and drinks: table accessories', 'Food consumption: cutlery and tools'], dtype=object)3. Using
describefunction on this column shows there are 3410 samples with 7 unique classifications.ds["l2_class"].describe()count 3410 unique 7 top Food consumption: plate, dish, bowl freq 2144 Name: l2_class, dtype: object4. Using a combination of
isnaandsumfunction on the dataset shows that some columns have a lot of NaNs.ds.isna().sum()find_number 0 material 0 start_date 0 end_date 0 l2_class 0 object_diameter 0 object_height 0 ceramics_image_type 2413 ceramics_mark 3308 on_website 0 material_simplified 0 url 2652 dtype: int64
Input and Output Selection
Now that we have familiarized ourselves with the dataset we can select the data attributes to use as input for the neural network and the target that we want to predict.
Choice of Input and Output
Inspect the dataset and identify suitable input features and output
Solution
A few possible comments:
- Columns
object_diameterandobject_heightcan be good features.- Columns
ceramics_image_typeandceramics_markfor example are not good features due to very high number of NaNs.- Columns
start_dateandend_dateare do not make good features as they are not related to the classification we want to achieve.
In the rest of this episode we will use the object_diameter, object_height, material_simplified attributes.
The target for the classification task will be the l2_class.
Data Exploration
Exploring the data is an important step to familiarize yourself with the problem and to help you determine the relevant inputs and outputs.
3. Prepare data
Remove unnecessary columns of data
The dataset currently contains a lot of redundant or unnecessary data columns. We will remove all columns except our input and output columns.
ds_preprocessed = ds[['l2_class', 'object_diameter', 'object_height', 'material_simplified']]
The input data and target data are not yet in a format that is suitable to use for training a neural network.
Clean missing values
During the exploration phase we saw that some rows in the dataset have missing (NaN)
values, leaving such values in the input data will ruin the training, so we need to deal with them.
There are many ways to deal with missing values, but for now we will just remove the offending rows by adding a call to dropna():
# Drop the rows that have NaN values in them
ds_preprocessed = ds_preprocessed.dropna()
Simplify output
Let’s explore the output classification column by looking at the number of data rows for each unique classification using the value_counts pandas function.
ds_preprocessed['l2_class'].value_counts()
Food consumption: plate, dish, bowl 2144
Consumption: drinking 874
Food preparation: cooking - and hearth utensils 255
Food preparation and consumption: various parts of kitchenware 107
Consumption of food and drinks: table accessories 24
Consumption of tobacco and stimulants 4
Food consumption: cutlery and tools 2
Name: l2_class, dtype: int64
There are two categories with notable data points in Food consumption: plate, dish, bowl and Consumption: drinking. We will focus on these for our neural network. To remove the others we will query the pandas dataframe.
ds_preprocessed = ds_preprocessed.query("l2_class == ['Consumption: drinking', 'Food consumption: plate, dish, bowl']")
Change output type if needed
The output column is our categorical target, however pandas still sees it as the
generic type Object. We can convert this to the pandas categorical type:
ds_preprocessed['l2_class'] = ds_preprocessed['l2_class'].astype('category')
This will make later interaction with this column a little easier.
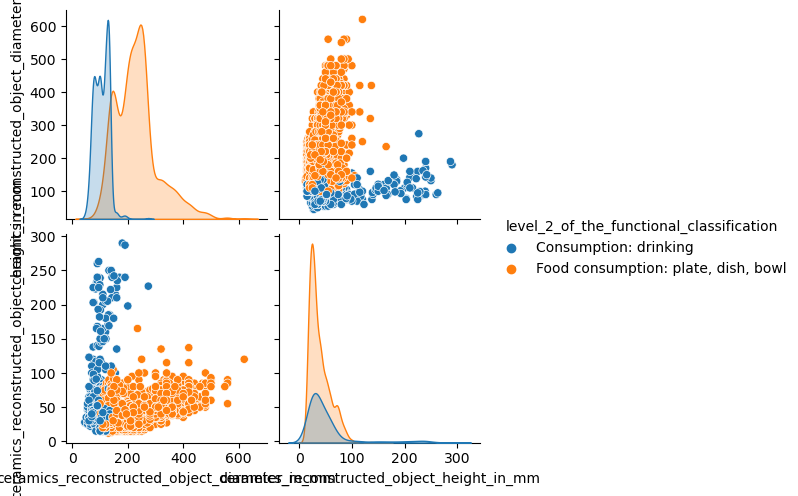
Pairplot: Visual Aid
Looking at numbers on a screen usually does not give a very good intuition about the data we are working with. So let us use a visualization tool called Pairplot which is useful for datasets with relatively few attributes. This can be created using
sns.pairplot(...)which can be imported from the seaborn package. It shows a scatterplot of each attribute plotted against each of the other attributes.import seaborn as sns sns.pairplot(ds_preprocessed, hue = 'l2_class')
Prepare target data for training
Second, the target data is also in a format that cannot be used in training.
A neural network can only take numerical inputs and outputs, and learns by
calculating how “far away” the species predicted by the neural network is
from the true species.
When the target is a string category column as we have here it is very difficult to determine this “distance” or error.
Therefore we will transform this column into a more suitable format.
Again there are many ways to do this, however we will be using the one-hot encoding.
This encoding creates multiple columns, as many as there are unique values, and
puts a 1 in the column with the corresponding correct class, and 0’s in
the other columns.
For instance, for a classification of the Consumption: drinking type, the one-hot encoding would be 0 1
Fortunately pandas is able to generate this encoding for us.
target = pd.get_dummies(ds_preprocessed['l2_class'])
target.head() # print out the top 5 to see what it looks like.
Prepare input data for training
Similar to the target column l2_class, we also have the material_simplified feature column which is a string and needs to be one-hot encoded. Let us first look at the unique values in the column.
ds_preprocessed['material_simplified'].unique()
Let us now convert the string input in to a categorical input and perform the one-hot encoding of the results.
ds_preprocessed['material_categorized'] = ds_preprocessed['material_simplified'].astype('category')
ds_features = pd.get_dummies(ds_preprocessed['material_categorized'])
Let us now combine all the features to create one input feature dataset
ds_features = ds_features.join(ds_preprocessed.drop(columns=['l2_class', 'material_simplified', 'material_categorized']))
One-hot encoding vs ordinal encoding
- How many output neurons will our network have now that we one-hot encoded the target class?
- Another encoding method is ‘ordinal encoding’. Here the variable is represented by a single column, where each category is represented by a different integer (0, 1 in this case). How many output neurons will a network have when ordinal encoding is used?
Solution
- 2, one for each output variable class
- 1, the 2 classes are represented in a single variable
Split data into training and test set
Finally, we will split the dataset into a training set and a test set. As the names imply we will use the training set to train the neural network, while the test set is kept separate. We will use the test set to assess the performance of the trained neural network on unseen samples. In many cases a validation set is also kept separate from the training and test sets (i.e. the dataset is split into 3 parts). This validation set is then used to select the values of the parameters of the neural network and the training methods. For this episode we will keep it at just a training and test set however.
To split the cleaned dataset into a training and test set we will use a very convenient
function from sklearn called train_test_split.
The output of the function are:
- the input features of the dataset for training (
X_train) and testing (X_test) and the corresponding training targets (y_train) and test targets (y_test).
This function takes a number of input parameters:
- The first two are the dataset (i.e. features) and the corresponding targets.
- Next is the named parameter
test_sizethis is the fraction of the dataset that is used for testing, in this case0.2means 20% of the data will be used for testing. random_statecontrols the shuffling of the dataset, setting this value will reproduce the same results (assuming you give the same integer) every time it is called.shufflewhich can be eitherTrueorFalse, it controls whether the order of the rows of the dataset is shuffled before splitting. It defaults toTrue. Note that it shuffles the rows but keeps the integrity of each row.stratifyis a more advanced parameter that controls how the split is done. By setting it totargetthe train and test sets the function will return will have roughly the same proportions (with regards to the number of second level classification) as the dataset.
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(ds_features, target,test_size=0.2, random_state=0, shuffle=True, stratify=target)
Training and Test sets
Take a look at the training and test set we created.
- How many samples do the training and test sets have?
- Are the classes in the training set well balanced?
Solution
Using
y_train.shapeandy_test.shapewe can see the training set has 273 samples and y_test has 69 samples.We can check the balance of classes by counting the number of ones for each of the columns in the one-hot-encoded target, which shows the training set has 699 data points for
Consumption: drinking, and 1715 forFood consumption: plate, dish, bowl.y_train.sum()Consumption: drinking 699 Food consumption: plate, dish, bowl 1715 dtype: int64The dataset is not perfectly balanced, but it is not orders of magnitude out of balance either. So we will leave it as it is.
4. Build an architecture from scratch or choose a pretrained model
Keras for neural networks
For this lesson we will be using Keras to define and train our neural network
models.
Keras is a machine learning framework with ease of use as one of its main features.
It is part of the tensorflow python package and can be imported using from tensorflow import keras.
Keras includes functions, classes and definitions to define deep learning models, cost functions and optimizers (optimizers are used to train a model).
Before we move on to the next section of the workflow we need to make sure we have Keras imported. We do this as follows:
from tensorflow import keras
For this class it is useful if everyone gets the same results from their training. Keras uses a random number generator at certain points during its execution. Therefore we will need to set two random seeds, one for numpy and one for tensorflow:
from numpy.random import seed
seed(1)
from tensorflow.random import set_seed
set_seed(2)
Build a neural network from scratch
We will now build out first neural network from scratch. Although this sounds like a daunting task, you will experience that with Keras it is actually surprisingly straightforward.
With Keras you compose a neural network by creating layers and linking them
together. For now we will only use one type of layer called a fully connected
or Dense layer. In Keras this is defined by the keras.layers.Dense class.
A dense layer has a number of neurons, which is a parameter you can choose when you create the layer. When connecting the layer to its input and output layers every neuron in the dense layer gets an edge (i.e. connection) to all of the input neurons and all of the output neurons. The hidden layer in the image in the introduction of this episode is a Dense layer.
The input in Keras also gets special treatment, Keras automatically calculates the number of inputs
and outputs a layer needs and therefore how many edges need to be created.
This means we need to let Keras now how big our input is going to be.
We do this by instantiating a keras.Input class and tell it how big our input is.
inputs = keras.Input(shape=X_train.shape[1])
We store a reference to this input class in a variable so we can pass it to the creation of our hidden layer. Creating the hidden layer can then be done as follows:
hidden_layer = keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="relu")(inputs)
The instantiation here has 2 parameters and a seemingly strange combination of parentheses, so
let us take a closer look.
The first parameter 10 is the number of neurons we want in this layer, this is one of the
hyperparameters of our system and needs to be chosen carefully. We will get back to this in the section
on hyperparameter tuning.
The second parameter is the activation function to use, here we choose relu which is 0
for inputs that are 0 and below and the identity function (returning the same value)
for inputs above 0.
This is a commonly used activation function in deep neural networks that is proven to work well.
Next we see an extra set of parenthenses with inputs in them, this means that after creating an
instance of the Dense layer we call it as if it was a function.
This tells the Dense layer to connect the layer passed as a parameter, in this case the inputs.
Finally we store a reference so we can pass it to the output layer in a minute.
Now we create another layer that will be our output layer. Again we use a Dense layer and so the call is very similar to the previous one.
output_layer = keras.layers.Dense(2, activation="softmax")(hidden_layer)
Because we chose the one-hot encoding, we use 2 neurons for the output layer.
The softmax activation ensures that the two output neurons produce values in the range (0, 1) and they sum to 1. We can interpret this as a kind of ‘probability’ that the sample belongs to a certain species.
Now that we have defined the layers of our neural network we can combine them into a Keras model which facilitates training the network.
model = keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=output_layer)
model.summary()
The model summary here can show you some information about the neural network we have defined.
Create the neural network
With the code snippets above, we defined a Keras model with 1 hidden layer with 10 neurons and an output layer with 2 neurons.
- How many parameters does the resulting model have?
- What happens to the number of parameters if we increase or decrease the number of neurons in the hidden layer?
Solution
inputs = keras.Input(shape=X_train.shape[1]) hidden_layer = keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="relu")(inputs) output_layer = keras.layers.Dense(2, activation="softmax")(hidden_layer) model = keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=output_layer) model.summary()Model: "model" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 10)] 0 _________________________________________________________________ dense (Dense) (None, 10) 110 _________________________________________________________________ dense_1 (Dense) (None, 2) 22 ================================================================= Total params: 132 Trainable params: 132 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________The model has 132 trainable parameters. If you increase the number of neurons in the hidden layer the number of trainable parameters in both the hidden and output layer increases or decreases accordingly of neurons. The name in quotes within the string
Model: "model"may be different in your view; this detail is not important.
How to choose an architecture?
Even for this small neural network, we had to make a choice on the number of hidden neurons. Other choices to be made are the number of layers and type of layers (as we will see later). You might wonder how you should make these architectural choices. Unfortunately, there are no clear rules to follow here, and it often boils down to a lot of trial and error. However, it is recommended to look what others have done with similar datasets and problems. Another best practice is to start with a relatively simple architecture. Once running start to add layers and tweak the network to see if performance increases.
Choose a pretrained model
If your data and problem is very similar to what others have done, you can often use a pretrained network. Even if your problem is different, but the data type is common (for example images), you can use a pretrained network and finetune it for your problem. A large number of openly available pretrained networks can be found in the Model Zoo, pytorch hub or tensorflow hub.
5. Choose a loss function and optimizer
We have now designed a neural network that in theory we should be able to train to classify our archeological finds. However, we first need to select an appropriate loss function that we will use during training. This loss function tells the training algorithm how wrong, or how ‘far away’ from the true value the predicted value is.
For the one-hot encoding that we selected before a fitting loss function is the Categorical Crossentropy loss.
In Keras this is implemented in the keras.losses.CategoricalCrossentropy class.
This loss function works well in combination with the softmax activation function
we chose earlier.
The Categorical Crossentropy works by comparing the probabilities that the
neural network predicts with ‘true’ probabilities that we generated using the one-hot encoding.
This is a measure for how close the distribution of the two neural network outputs corresponds to the distribution of the two values in the one-hot encoding.
It is lower if the distributions are more similar.
For more information on the available loss functions in Keras you can check the documentation.
Next we need to choose which optimizer to use and, if this optimizer has parameters, what values to use for those. Furthermore, we need to specify how many times to show the training samples to the optimizer.
Once more, Keras gives us plenty of choices all of which have their own pros and cons, but for now let us go with the widely used Adam optimizer. Adam has a number of parameters, but the default values work well for most problems. So we will use it with its default parameters.
Combining this with the loss function we decided on earlier we can now compile the
model using model.compile.
Compiling the model prepares it to start the training.
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss=keras.losses.CategoricalCrossentropy())
6. Train model
We are now ready to train the model.
Training the model is done using the fit method, it takes the input data and
target data as inputs and it has several other parameters for certain options
of the training.
Here we only set a different number of epochs.
One training epoch means that every sample in the training data has been shown
to the neural network and used to update its parameters.
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=100)
The fit method returns a history object that has a history attribute with the training loss and potentially other metrics per training epoch. It can be very insightful to plot the training loss to see how the training progresses. Using seaborn we can do this as follow:
sns.lineplot(x=history.epoch, y=history.history['loss'])
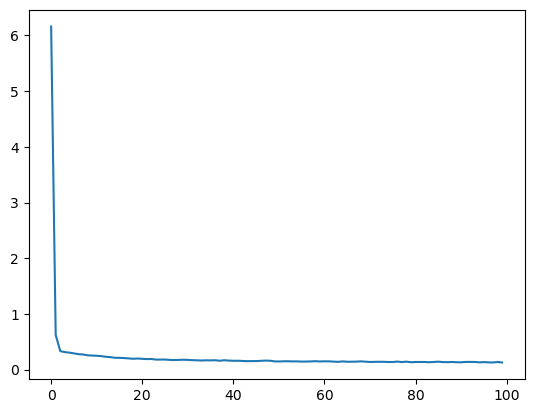
This plot can be used to identify whether the training is well configured or whether there are problems that need to be addressed.
The Training Curve
Looking at the training curve we have just made.
- How does the training progress?
- Does the training loss increase or decrease?
- Does it change fast or slowly?
- Is the graph look very jittery?
- Do you think the resulting trained network will work well on the test set?
Solution
- The loss curve should drop quite quickly in a smooth line with little jitter
- The results of the training give very little information on its performance on a test set. You should be careful not to use it as an indication of a well trained network.
7. Perform a prediction/classification
Now that we have a trained neural network, we can use it to predict new samples using the predict function.
We will use the neural network to predict the second level classification of the test set
using the predict function.
We will be using this prediction in the next step to measure the performance of our
trained network.
This will return a numpy matrix, which we convert
to a pandas dataframe to easily see the labels.
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
prediction = pd.DataFrame(y_pred, columns=target.columns)
prediction
Output
Consumption: drinking Food consumption: plate, dish, bowl 0 1.192648e-18 9.999999e-01 1 2.878897e-04 9.997121e-01 2 9.933218e-01 6.678253e-03 3 1.550273e-11 9.999999e-01 4 9.999999e-01 1.860956e-36 ... ... ... 599 4.948534e-01 5.051466e-01 600 1.249560e-04 9.998751e-01 601 1.192672e-03 9.988073e-01 602 9.193144e-01 8.068555e-02 603 1.893464e-01 8.106536e-01 604 rows × 2 columns
Remember that the output of the network uses the softmax activation function and has two
outputs, one for each classification. This dataframe shows this nicely.
We now need to transform this output to one classification type per sample.
We can do this by looking for the index of highest valued output and converting that
to the corresponding classification.
Pandas dataframes have the idxmax function, which will do exactly that.
predicted_class = prediction.idxmax(axis="columns")
predicted_class
Output
0 Food consumption: plate, dish, bowl 1 Food consumption: plate, dish, bowl 2 Consumption: drinking 3 Food consumption: plate, dish, bowl 4 Consumption: drinking ... 599 Food consumption: plate, dish, bowl 600 Food consumption: plate, dish, bowl 601 Food consumption: plate, dish, bowl 602 Consumption: drinking 603 Food consumption: plate, dish, bowl Length: 604, dtype: object
8. Measuring performance
Now that we have a trained neural network it is important to assess how well it performs. We want to know how well it will perform in a realistic prediction scenario, measuring performance will also come back when tuning the hyperparameters.
We have created a test set during the data preparation stage X_test and y_test, which we will use now to create a confusion matrix.
Confusion matrix
With the predicted classification we can now create a confusion matrix and display it
using seaborn.
To create a confusion matrix we will use another convenient function from sklearn
called confusion_matrix.
This function takes as a first parameter the true labels of the test set.
We can get these by using the idxmax method on the y_test dataframe.
The second parameter is the predicted labels which we did above.
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
true_class = y_test.idxmax(axis="columns")
matrix = confusion_matrix(true_class, predicted_class)
print(matrix)
[[169 6]
[ 7 422]]
Unfortunately, this matrix is kinda hard to read. Its not clear which column and which row corresponds to which class. So let’s convert it to a pandas dataframe with its index and columns set to the classes as follows:
# Convert to a pandas dataframe
confusion_df = pd.DataFrame(matrix, index=y_test.columns.values, columns=y_test.columns.values)
# Set the names of the x and y axis, this helps with the readability of the heatmap.
confusion_df.index.name = 'True Label'
confusion_df.columns.name = 'Predicted Label'
We can then use the heatmap function from seaborn to create a nice visualization of
the confusion matrix.
The annot=True parameter here will put the numbers from the confusion matrix in
the heatmap.
sns.heatmap(confusion_df, annot=True)
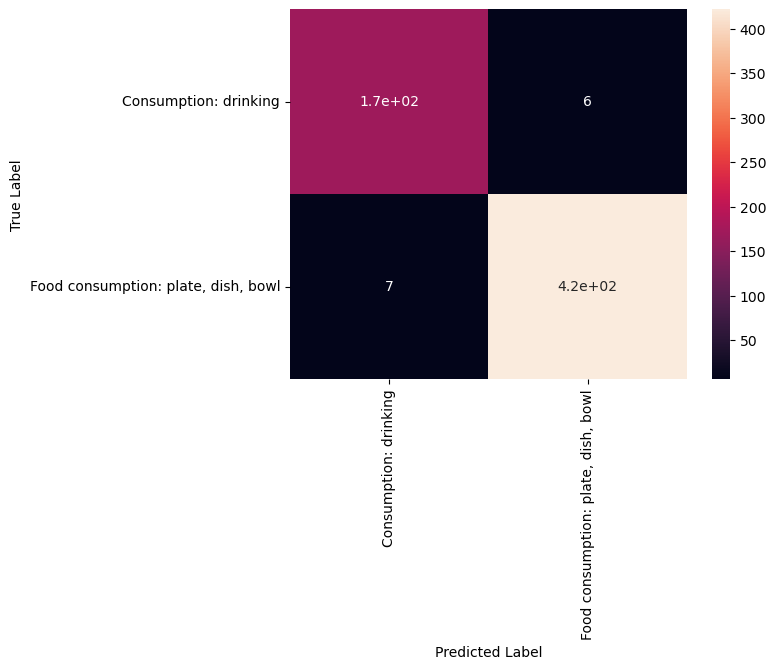
Confusion Matrix
Measure the performance of the neural network you trained and visualize a confusion matrix.
- Did the neural network perform well on the test set?
- Did you expect this from the training loss you saw?
- What could we do to improve the performance?
Solution
The confusion matrix shows that the predictions for the two classes are quite accurate, but could be improved.
The training loss was very low, so from that perspective this may be expected. But always keep in mind that a good training loss does not ensure excellent performance on new data set. That is why a test set is important when training neural networks.
We can try many things to improve the performance from here. One of the first things we can try is to balance the dataset better. Other options include: changing the network architecture or changing the training parameters
9. Tune hyperparameters
As we discussed before the design and training of a neural network comes with many hyper parameter choices. We will go into more depth of these hyperparameters in later episodes. For now it is important to realize that the parameters we chose were somewhat arbitrary and more careful consideration needs to be taken to pick hyperparameter values.
10. Share model
It is very useful to be able to use the trained neural network at a later
stage without having to retrain it.
This can be done by using the save method of the model.
It takes a string as a parameter which is the path of a directory where the model is stored.
model.save('my_first_model')
This saved model can be loaded again by using the load_model method as follows:
pretrained_model = keras.models.load_model('my_first_model')
This loaded model can be used as before to predict.
# use the pretrained model here
y_pretrained_pred = pretrained_model.predict(X_test)
pretrained_prediction = pd.DataFrame(y_pretrained_pred, columns=target.columns.values)
# idxmax will select the column for each row with the highest value
pretrained_predicted_class = pretrained_prediction.idxmax(axis="columns")
print(pretrained_predicted_class)
Key Points
The deep learning workflow is a useful tool to structure your approach, it helps to make sure you do not forget any important steps.
Exploring the data is an important step to familiarize yourself with the problem and to help you determine the relavent inputs and outputs.
One-hot encoding is a preprocessing step to prepare labels for classification in Keras.
A fully connected layer is a layer which has connections to all neurons in the previous and subsequent layers.
keras.layers.Dense is an implementation of a fully connected layer, you can set the number of neurons in the layer and the activation function used.
To train a neural network with Keras we need to first define the network using layers and the Model class. Then we can train it using the model.fit function.
Plotting the loss curve can be used to identify and troubleshoot the training process.
The loss curve on the training set does not provide any information on how well a network performs in a real setting.
Creating a confusion matrix with results from a test set gives better insight into the network’s performance.